AMPDs wound healing
Biopolymers and antimicrobial peptide dendrimers (AMPDs) work in synergy towards wound protection, healing and regeneration
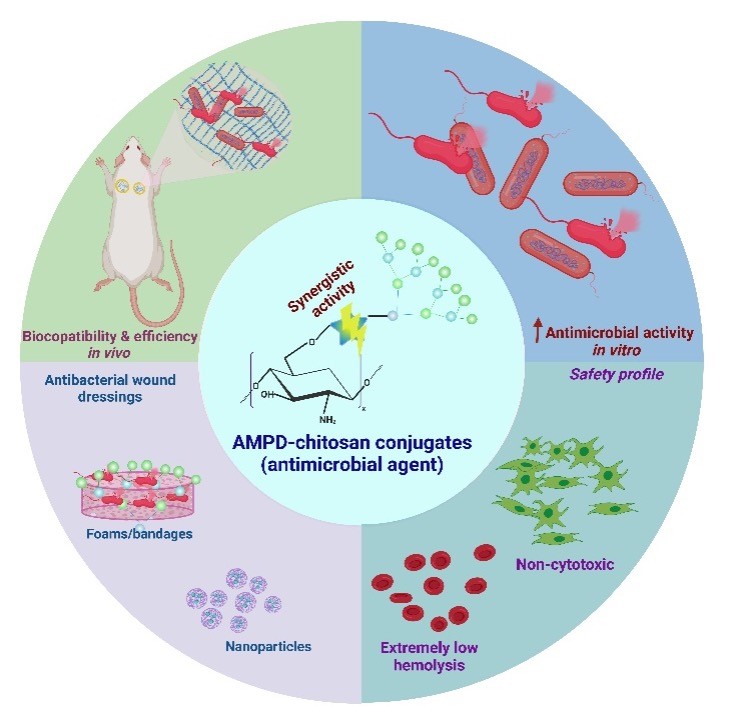
The burden of bacterial wound infections has increased significantly due to antibiotic resistance to most currently available antimicrobial drugs. Within this project, a new chemical platform for coupling chitosan derivatives to antimicrobial peptide dendrimers (AMPDs) has been developed.
The AMPD-chitosan conjugates act synergistically to destroy bacteria, without any loss of antimicrobial activity. These new proprietary “active principles” were successfully incorporated into various biopolymer-based formulations, including nanoparticles, gels, and foams.
In vivo studies conducted in both healthy and infected murine models demonstrated the potent antibacterial performance of the developed dressings. This versatile chemical technology platform provides a promising foundation for the design of new membrane-disruptive therapeutics aimed at eliminating pathogens associated with acute and chronic wounds.
Project Members: Dr Viorica Patrulea, Dr Geoffrey Depaepe, Dr Olivier Jordan, Prof Gerrit Borchard
External collaborators: Prof Jean-Louis Reymond (University of Bern, Switzerland), PhD Nikitha Vavilthota, Prof Sebastianus Zaat and Prof Martijn Riool (Amsterdam Medical Center, The Netherlands), Prof Takehisa Hanawa (Tokyo University of Science, Japan), Dr Marlène Durand (CIC-IT, Bordeaux, France), Prof Cintia Cristina Martignago (University of Brazil, Brazil).
Keywords : antimicrobial peptide/dendrimers (AMP/AMPDs), wound healing, tissue regeneration, wound dressings, antimicrobial resistance