Stabilization mRNA formulations
Stabilization of mRNA formulations
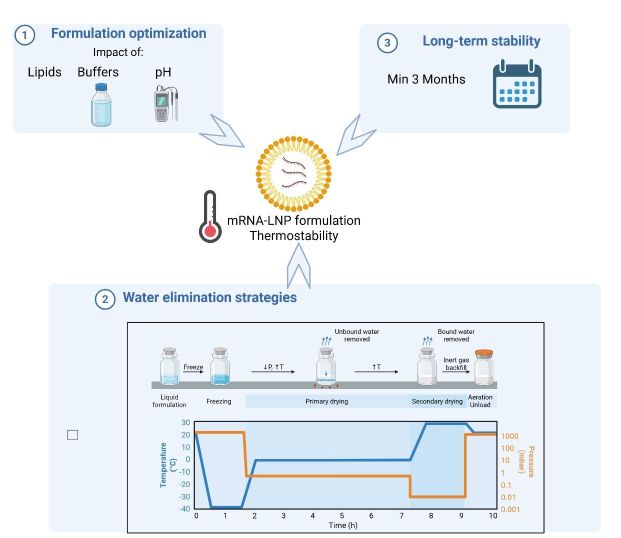
In recent years, mRNA-LNP therapies transitioned from a doubtful concept to clinical success, as demonstrated by Spikevax® (Moderna) and Comirnaty® (Pfizer-BioNTech) that became vaccine front-runners during the Covid-19 pandemic due to their rapid development. As a result, mRNA-based therapies gained significant investments from pharmaceutical industries with 77% of mRNA companies having at least one prophylactic vaccine in their pipeline. Nevertheless, critical challenges remain, such as the reliance on costly ultracold storage, which limits the access to low- and middle-income countries, contributes to the emergence of new serotypes of the virus, and results in the discard of many expired vaccines. The aim of this research work is to address these issues by enhancing the stability of the mRNA-LNP formulations at 4°C or room temperature, through the investigation of multiple water removal strategies, and the optimization of the formulation.
Project Members: Aya Halmi, Dr. Olivier Jordan, Prof. Gerrit Borchard
External collaborators: Pr Alf Lamprecht (Bonn University, DE)
Keywords: nucleic acid vaccines, lipid-based nanosystems, lyophilization, spray-freeze drying