HDAC6 in lung cancer
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths and one of the most diagnosed cancers worldwide. Despite the wide range of therapeutic and surgical options, lung cancer patients often face poor prognosis and are only diagnosed at advanced stages of progression. Therefore, there is a strong need to broaden the range of therapeutic options against this malignancy. Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) has been suggested to play an important role in cancer due to its ability to deacetylase and regulate several non-histone proteins in the cytoplasm. It has been associated with several oncogenic functions in different cancer types, such as cell stress response, proliferation, metastasis and resistance. Its inhibition has been reported to sensitize cells to various anti-cancer treatments, hence constituting a promising target for combination therapies. The fundamental research in our group aims to get insight into the role of HDAC6 in lung adenocarcinoma, to decipher interacting pathways and to find potential HDAC6 partners for drug combinations.
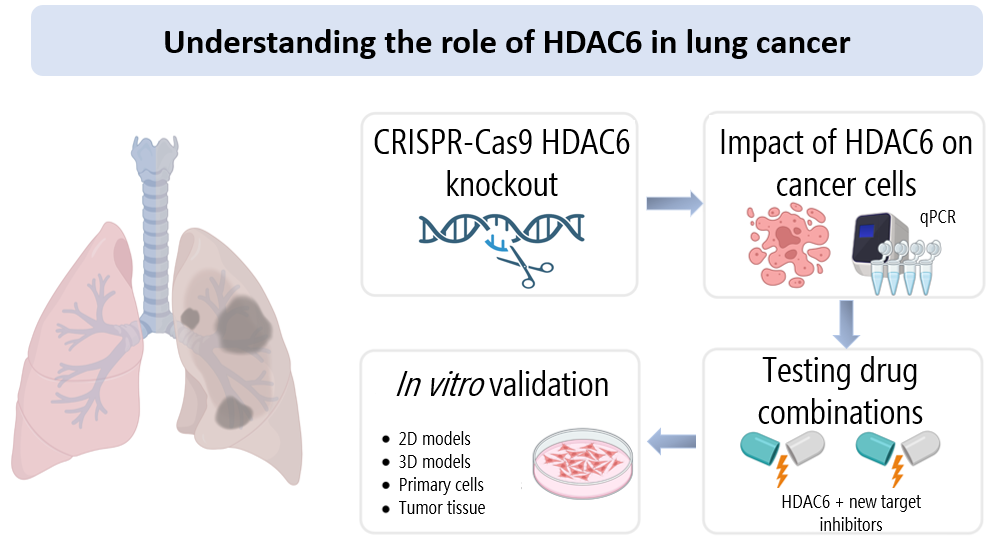
Figure created with BioRender.com